The language content is nearly always determined by the coursebook and/or syllabus. The unique needs of each learner are not taken into consideration when the language is taught and practiced. Because of this, after experimenting with the PPP (Presentation, Practice, Production) approach, many educators who have undergone an online teacher training course in Singaporeswitched to more learner-centered methods in which the needs of the student are at the center of the lesson’s content.
Task-Based Learning (TBL) and Project-Based Learning (PBL) are two examples of these methods. Explore all the details of these two approaches along with their significant differences.
What Is Task-Based Learning?
Source: barefootteflteacher.com
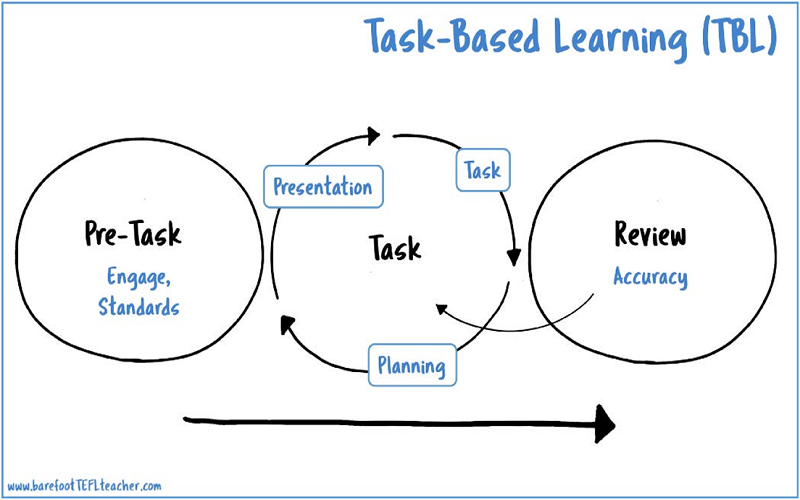
Task-based learning centers on completing designated tasks to meet language learning objectives. By giving them relevant and genuine assignments that reflect real-world situations, teachers help students improve their language proficiency via hands-on practice. TBL actively encourages students to participate in language creation and interaction by placing a high priority on communicative ability. Through task-based learning, TBL fosters language correctness, fluency, and pragmatic competence in pupils.
What Is Project-Based Learning?

Source:itl-institute.com
On the other hand, project-based learning centers on the execution of lengthy, complex projects that incorporate a variety of subject areas and skill sets. Pupils are given difficult, real-world challenges or difficulties, and they collaborate to plan and carry out projects that solve these problems. PBL fosters creativity, inquiry, investigation, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. It encourages the growth of vital 21st-century abilities including self-directed learning, teamwork, and communication.
5 Significant Differences Between PBL And TBL Every Teacher Must Know
Here are a few distinct characteristics of TBL and PBL that offer a comprehensive understanding along with unique learner benefits:
1. Characteristics And Approaches
Task-Based Learning:
The TBL strategy is focused on completing designated tasks. The exercises are designed to seem like real-world scenarios and provide students with chances to practice using the language in genuine settings. The improvement of linguistic abilities through task completion is the main objective. TBL motivates students to actively participate in meaning negotiation, interaction, and language production. It encourages the growth of accurate language use, fluency, and pragmatic competence.
Task-Based Learning involves assigning students tasks that need them to utilize the target language to accomplish a certain objective. These assignments may take the form of genuine activities that students could participate in outside of the classroom or simulations of actual scenarios.
Project Based Learning:
PBL entails carrying out lengthy projects that deal with issues or obstacles that arise in the actual world. Inquiry, investigation, critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity are prioritized. PBL fosters teamwork, in-depth analysis, and creative problem-solving among students. It fosters the growth of 21st-century abilities including self-directed learning, communication, and teamwork.
Through Project-Based Learning, students delve deeply into an intricate subject or issue. Together, they choose a topic or problem to investigate, carry out the study, and create a project that takes on the challenge. PBL empowers students to take charge of their education, draw connections across different subject areas, and use what they’ve learned in real-world situations.
1. Learning Objectives:
Task-Based Learning:
The development of language proficiency and communicative competence is the main learning goal of TBL. They improve their capacity for appropriate, accurate, and fluent self-expression. The language functions, grammatical rules, and vocabulary that are necessary for clear communication are encouraged to be acquired through TBL.
Additionally, via comprehending and using language in social and cultural situations, TBL supports learners in gaining pragmatic competence. Students who participate in Task-Based Learning not only enhance their language proficiency but also acquire critical communication skills. They gain the ability to explain knowledge, negotiate meaning, and voice their ideas.
Project Based Learning:
PBL’s learning goals extend beyond only mastering a language. PBL seeks to develop 21st-century skills, problem-solving abilities, and critical thinking. Students get experience in doing research, analyzing complicated issues, and applying knowledge from a variety of fields via project work. PBL fosters invention, creativity, and the growth of strong teamwork and communication abilities.
Through project-based learning, students are tasked with applying critical thinking and problem-solving skills to real-world, genuine problems. They gain knowledge on how to get data, assess sources, ask insightful questions, and come to well-informed conclusions. PBL encourages students to work together and enhance their problem-solving abilities as they take on challenging problems.
2. Scope And Timeframe
Task-Based Learning:
Generally, task-based learning entails shorter, more targeted assignments with clear language learning objectives. These assignments are meant to be finished in one or more class sessions, or in a comparatively short amount of time. With TBL, students may practice language in specific areas and build their skills, giving them timely feedback and chances to grow better.
Project Based Learning:
Extended projects with wider learning goals are a feature of project-based learning. It takes more time to design, carry out, and finish these undertakings. PBL might take many weeks or even months, depending on the project’s complexity and scale. PBL gives students the chance to investigate a topic or issue more thoroughly, which facilitates the development of a thorough grasp of the subject and a complete solution.
3. Organization And Structure
Task-Based Learning:
TBL usually adheres to a well-defined job sequence to promote language learning and advancement. The scaffolding of the tasks enables students to build on the information and abilities they already possess.
Pre-task exercises to draw on past knowledge, task performance exercises where students do the primary job, and post-task exercises for introspection and feedback are all common components of task-based learning (TBL). This methodical technique guarantees a methodical progression in language acquisition and aids in the steady development of language competency in learners.
Project Based Learning:
PBL is distinguished by its flexible and open-ended framework. To foster creativity and student autonomy, students are allowed the flexibility to experiment and make judgments about how to approach the assignment.
Multiple phases, such as project planning, research, design, execution, and presentation, are frequently included in PBL. Students work together, assume responsibilities, and often reflect on and assess their development. Because PBL is adaptable, students may make changes if they run into obstacles or learn new knowledge while working on the project.
4.Teacher And Student Roles
Task-Based Learning:
In TBL, the instructor facilitates learning by supporting and guiding students while they work on assignments. It is the responsibility of the instructor to design an exciting and engaging learning environment, choose appropriate assignments, and give clear directions. They also foster reflection on the learning process, provide feedback on language use, and keep track of students’ development.
Students actively participate in their learning when they engage in TBL. They collaborate with their peers by having talks, negotiating, and working through issues together. It is the responsibility of the students to organize their work, make choices, and use language in real-world situations. TBL promotes learner autonomy by letting students take charge of their education through goal-setting, progress tracking, and language development reflection.
Project Based Learning:
The instructor takes on the roles of both guide and facilitator in PBL. By outlining the project’s concept, creating learning objectives, and laying out expectations clearly, they offer first guidance. The instructor helps the students define the parameters of the project, find relevant materials, and create a plan. Throughout the assignment, they provide feedback and direction to help students stay on task and fulfill the required learning objectives.
Project-based learning involves the active and central participation of students. They work together as a team, delegating tasks and utilizing one another’s advantages. Students conduct research, gather data, analyze it, and solve problems by using their knowledge and abilities to come up with creative solutions. PBL fosters critical thinking, informed decision-making, and effective concept communication in students.
Which Approach Is Better?
Knowing the distinctions between TBL and PBL enables teachers to choose the strategy that best suits their student’s needs and their own learning goals. Teachers who have completed Teacher Training in Singapore may design engaging and stimulating learning experiences that enable students to become lifelong learners and problem solvers, whether through task completion or project execution.



